
 |
Leprosy
Site: St. John's, Timberhill (part of Castle Mall), Norwich
Period: Late Saxon to post-medieval.
Excavator: Norfolk Archaeological Unit.
Published: forthcoming.
Skeleton: male, c.16-20 years.
Catalogue entry: The evidence for leprosy in this individual was strong: The face: there was pitting around the nasal aperture and front teeth. - The hands: in the left hand (see photo above), the metacarpals were pitted at the distal ends and articular surfaces, there were deep VPGs on the proximal phalanges and the articular surfaces were destroyed, suggesting pyogenic arthritis and claw-hand deformity. The distal end of thumb phalanx was almost totally destroyed. Some concentric diaphyseal remodelling of the middle phalanges had occurred, and there was graining especially dorsally, VPGs, and septic arthritis at the proximal ends. The distal phalanx of the thumb was similar.
The three remaining proximal phalanges of the right hand had volar phalangeal grooves (VPG).
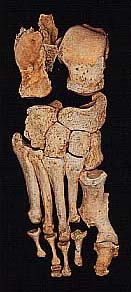
- The feet: in the right foot (see photo right), there was surface inflammatory pitting of all tarsal bones, and on the metatarsals slight pitting but more graining. No remodelling of the third to fifth metatarsals was present, but the distal ends showed absorption of cortical bone leaving the joint surfaces with a close-pitted appearance. Most graining and pitting has occurred in the distal third of the third metatarsal. The distal end of the second metatarsal was destroyed by septic arthritis, and the proximal phalanx shows similar but less gross changes. Septic arthritis of the first metatarso-phalangeal joint has resulted in loss of bone and ankylosis with claw-toe deformity. The distal phalanx is pitted and shows some remodelling at the distal end only. The proximal 2nd-4th phalanges show hourglass deformity.
In the left foot, the changes were less severe. Some periosteal graining of the distal thirds of the metatarsals and proximal halves of the proximal phalanges was noted. The proximal hallucial phalanx especially shows graining only on the dorsal proximal half. In addition, there was osteophytosis of the first metatarso-phalangeal joint and a small osteochondritic lesion on the proximal phalangeal articular surface.
- The legs: Periostitis of shins: graining and thickening of the right tibia, new bone growth on the distal half of the right fibula, also very slight on the left tibia and fibula.
|